by Cody Dumont
July 16, 2020
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) was developed to create a framework to assess an organization's implementation of cybersecurity practices evenly across the defense industrial base. Using NIST 800-53 and NIST 800-171 as the baseline, the primary objective of CMMC is to consolidate the two security catalogs into a single measurable framework. Over the next 5 years, starting in June 2020, organizations that create Government off-the-shelf (GOTS) products, handle Federal Contract Information (FCI), or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) will need to show compliance at Levels 1 through 5. Only Certified 3rd Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAO) will be able to certify an organization as compliant or not. Security Center provides on-prem solutions for assessing Cyber Exposure practices and maps these practices to known assessment regulations such as NIST, CSF, and others.
According to the CMMC documentation, “a maturity model is a set of characteristics, attributes, indicators, or patterns that represent capability and progression in a particular discipline.” Defining this model helps organizations modify their internal processes to align with CMMC, beginning with Level 1. At Level 1, the organization will be able to demonstrate how they perform at safeguarding FCI data. There are two primary requirements for Level 1:
- Processes: performs the specified practices
- Practices: Basic Cyber Hygiene, basic safeguarding requirements specified in 48 CFR 52.204-2
In building to higher levels the organization will improve processes and practices from an ad-hoc nature to a more documented and managed practice/process. Level 1 covers 17 practices across 6 security domains:
- Access Control (AC)
- Identification & Authentication (IA)
- Media Protection (MP)
- Physical Protection (PE)
- System & Communications Protection (SC)
- System & Information Integrity (SI)
Security Center helps the CISO and the security team discover and analyze many of the 17 practices required by Level 1. Using the combination of active, compliance, and passive scanning, the CISO is able to visualize the health of the security program and prepare for the Level 1 assessment by a C3PAO. Organizations can use the Cyber Exposure Lifecycle model to assist in the initial Level 1 assessment.
Cyber Exposure is an emerging discipline for managing and measuring cybersecurity risk. The first step, Discover, helps to identify the network using active and passive methods. This dashboard provides a list of networks that have been discovered, along with indicators of the system type. Followed by Assess & Analyze data is presented that helps to understand how hardening standards are followed, alongside the patching process tracking. The final steps are to Fix and Measure, which are highlighted in the remediation summary information provided along with common Service Level Agreements (SLA) metrics.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.12.0
- Nessus 8.9.0
- Compliance Data
- NNM 5.11.0
Security Center is the market-defining On-Prem Cyber Exposure Platform. Security Center provides the ability to continuously Assess an organization’s adherence to best practice configuration baselines. Security Center provides customers with a complete Cyber Exposure platform for completing effective cybersecurity practices prescribed by CMMC standard.
Components
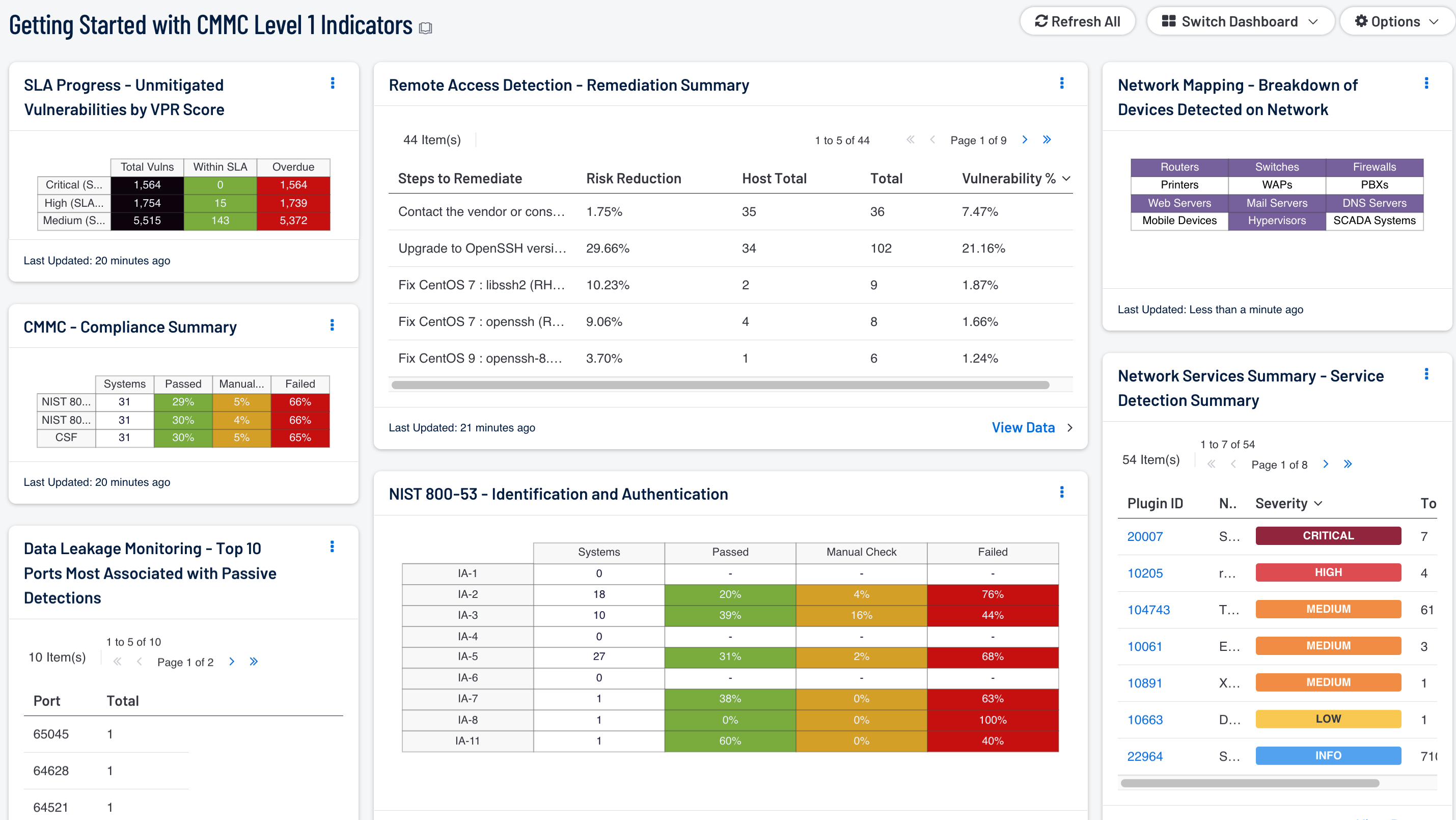
Remote Access Detection - Remediation Summary: This table provides information on vulnerability remediation solutions available for remote access vulnerabilities. Filters used within this component use associated CPE strings for applications associated with each remote access protocol, which provides a greater view for analysts to quickly detect vulnerabilities associated with these applications, and adds to the level of vulnerability detail provided to the organization. Each solution provides the percentage of risk reduction, the total hosts affected, and the percentage of vulnerabilities resolved. This component can be used to obtain a list of patches that can be installed to quickly remediate vulnerabilities and reduce risk.
Data Leakage Monitoring - Top 10 Ports Most Associated with Passive Detections: This table presents the top 10 ports associated with the most passive detections of data leakage. These passive detections are vulnerabilities reported by NNM in the 'Data Leakage' plugin family. The list is ordered so that the port associated with the worst data leakage is at the top. A count of detections and a bar graph indicating the severity of the detections are given for each port.
SLA Progress - Unmitigated Vulnerabilities by VPR Score: The matrix provides a summary of vulnerabilities based on the VPR score and the SLA of 30, 60, 90 days. Each of the three rows are based on the VPR severity from Medium to Critical. The three columns illustrate the count of vulnerabilities across all systems. To provide more focus to an asset group, the component can be installed with focus option set accordingly. The black cells are the count of vulnerabilities, with green meaning newly discovered and are within the prescribed SLA, while the red count are vulnerabilities that have been detected on the network for more than the allotted mitigation time.
CMMC - Compliance Summary: This component displays a summary of several audit standards (NIST 800-53, NIST 800-171, CSF), providing a host count, and ratio bars for each severity level. CMMC focuses on NIST 800-53 and NIST 800-171, at the same time Cyber Security Framework (CSF) is cross mapped with several other standards to provide a more holistic account of security compliance tracking. The three columns with ratio bars provide a ratio of total audit checks to a specified status of the check. Checks that have passed are green, failed checks are red, and checks which require manual verification are in orange.
NIST 800-53 - Identification and Authentication: The audit checks in the Identification and Authentication family primarily focus on the configuration settings concerned with authentication systems. The first column provides a count of systems with compliant checks, while the other three columns reflect the status of audit check using the ratio bar. Passed means the scan found the check to be within the defined parameter, while red means the check was outside of the defined parameter. Orange means the check requires a manual review of the data to determine pass or fail.
Network Mapping - Breakdown of Devices Detected on Network: This matrix presents a breakdown of detected network systems by type. A purple indicator denotes that systems of that type were detected; clicking on the indicator will bring up information on each of the detected systems, including IP address and MAC address. This information can assist an organization in maintaining an accurate inventory and detecting any unauthorized systems. The type of the network system is determined either based on its operating system (OS) or by the actively or passively detected vulnerabilities it has. Indicators are included for routers, switches, firewalls, printers, wireless access points (WAPs), PBXs, web servers, mail servers (IMAP, POP, and SMTP servers, as well as other specific servers such as Microsoft Exchange), DNS servers, mobile devices, hypervisors (virtual machines), and SCADA systems.
Network Services Summary - Service Detection Summary: This component presents a list of services detected on internal network hosts. Services presented within this table can include network protocols, databases, servers, remote desktop services, and more. Some of this information can also include insecure protocols such as FTP, Telnet, and SSL protocols. The table is sorted by severity which will allow for quick detection and remediation of insecure protocols by analysts. Analysts can modify the table to report on specific information per organizational requirements.