by Cody Dumont
July 16, 2020
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) was developed to create a framework to assess an organization's implementation of cybersecurity practices evenly across the defense industrial base. Using NIST 800-53 and NIST 800-171 as the baseline, the primary objective of CMMC is to consolidate the two security catalogs into a single measurable framework. Over the next 5 years, starting in June 2020, organizations that create Government off-the-shelf (GOTS) products, handle Federal Contract Information (FCI), or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) will need to show compliance at 1 of the 5 levels. Only Certified 3rd Party Assessment Organizations (C3PAO) will be able to certify an organization as compliant or not. Security Center provides on-prem solutions for assessing Cyber Exposure practices and maps these practices to known assessment regulations such as NIST, CSF, and others. This dashboard showcases practices from the Risk Management (RM), Security Assessment (CA), Situational Awareness (SA), and System & Communications Protection (SC) domains.
The CMMC defines Cybersecurity risk as "risk to organizational operations, resources, and other organizations due to the potential for unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction of information or IT." Securing the environment against what seems to be countless adversaries requires an adaptive risk management program. To assist in this process Tenable created the Vulnerability Priority Rating (VPR). Using a process called Predictive Prioritization, Tenable combines Tenable-collected vulnerability data with third-party vulnerability and threat data and analyzes them together with advanced data science algorithms developed by Tenable Research. Using this information the Risk Manager and CISO can work closely with the IT Operations team and other stakeholders in identifying the most critical risks to their organization. Whether the organization is a Level 1 or Level 5, this information can identify the most likely points of entry. By focusing on vulnerabilities that are currently being exploited in the wild, the overall risk to the organization will decrease.
Risk managers are also tasked with monitoring security controls on an ongoing basis (CA.3.161). CMMC requires a plan for monitoring and assessing recurring risk on a on-going basis. Security Center provides the ability to track assessment results over time and will continuously provide status updates on the current state of cyber assets. When assessing the risks to assets, Security Center tracks which common exploit frameworks can be leveraged to penetrate the asset. In addition, the date the patches are published, to aid in the creation of SLA’s, and facilitate reporting to executive management.
Security Center uses active and passive methods to evaluate risk to a system. CMMC requires scanning to be performed on a regular basis, and for most systems that can be actively scanned, this requirement is sustainable. However for more fragile systems that cannot be actively scanned, the Nessus Network Monitor can be used to monitor these systems for vulnerabilities and track behaviors, such as newly opened ports. Security Centerpulls all the cyber risk information together in one place to provide a clear picture of how the organization is progressing at risk mitigation.
The dashboard and its components are available in the Security Center Feed, a comprehensive collection of dashboards, reports, assurance report cards and assets. The dashboard can be easily located in the Security Center Feed under the category Compliance & Configuration Assessment. The dashboard requirements are:
- Security Center 5.12.0
- Nessus 8.9.0
- Compliance Data
Security Center is the market-defining On-Prem Cyber Exposure Platform. Using the Cyber Exposure Lifecycle organizations can manage cybersecurity risk through an informed decision-making process. Tracking vulnerabilities with active and passive scanning provides the metrics risk managers to successfully achieve an optimized cybersecurity practice prescribed by CMMC standard.
Components
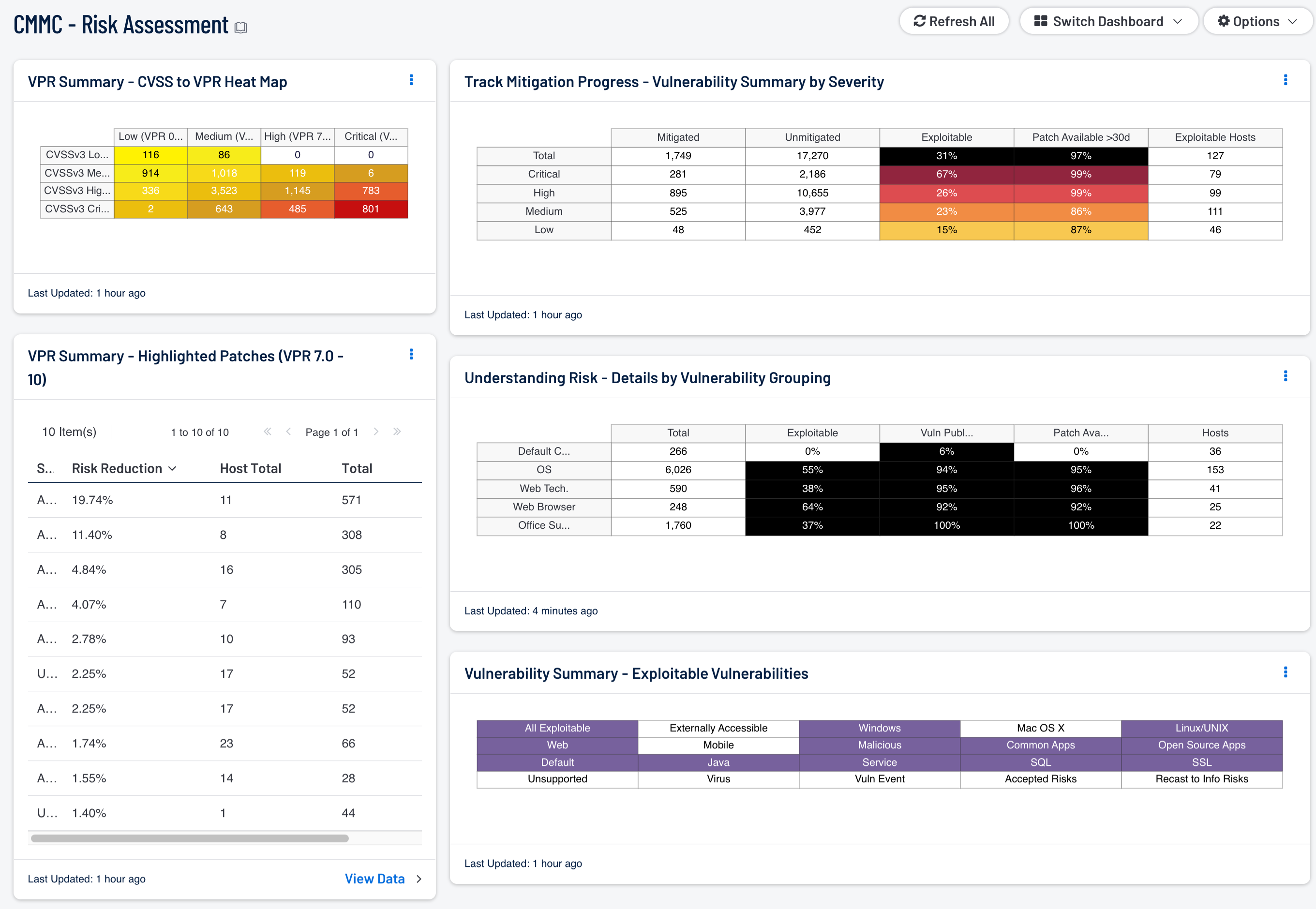
VPR Summary - CVSS to VPR Heat Map: This component provides a correlation between CVSSv3 scores and VPR scoring for the vulnerabilities present in the organization. The CVSSv3 scores are the traditional method of analyzing risk, while VPR is a new method based on data science analysis and threat modeling. Each cell is comprised of a combination of cross-mapping of CVSS & VPR scoring. Using a heat map approach, the filters begin in the left upper corner with vulnerabilities with the least risk. Moving to the right and lower down the matrix the colors change darker from yellow to red as the risk levels increase. Customers should mitigate risks in the lower right corners, and then work towards the upper left cells.
VPR Summary - Highlighted Patches (VPR 7.0 - 10): The component uses the High and Critical VPR levels (VPR 7.0 - 10) combined with the remediation summary tool to provide a focused view of patches that should be considered at a higher priority than other patches. The tool provides a list of patches to apply, the amount of risk reduced (based on vulnerability weight score), hosts affected, and percentage of vulnerabilities. Using Predictive Prioritization, organizations are able to better understand which vulnerabilities should be mitigated first. Combined with this comprehensive view Security Center provides the list of patches that can have the more immediate impact.
Track Mitigation Progress - Vulnerability Summary by Severity: Security Center records when vulnerabilities are discovered, when patches are issued, and when vulnerabilities are mitigated. This component assists in tracking vulnerability mitigations. In the matrix, the row with red is critical severity vulnerability information, the row with orange is high severity, the row with yellow is medium severity, and the row with green is low severity. The Mitigated column displays the number of vulnerabilities that have been moved to the mitigated database. A vulnerability is moved to the mitigated database when the vulnerability is no longer detected by a rescan; the vulnerability is assumed to be remediated. The Unmitigated column displays the number of current vulnerabilities that are not yet remediated and have not been moved to the mitigated database. The Exploitable column displays the percentage of those unmitigated vulnerabilities that are known to be exploitable. The Patch Available column displays the percentage of the unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities that have had a patch available for more than 30 days. Ideally, both of these percentages should be 0%, because all exploitable vulnerabilities and all vulnerabilities with patches available should have been mitigated already. The Exploitable Hosts column displays the number of hosts on the network that have unmitigated, exploitable vulnerabilities.
Understanding Risk - Details by Vulnerability Grouping: This matrix presents details by vulnerability grouping on vulnerabilities found to exist in the environment. For each vulnerability grouping, the number of vulnerabilities is displayed, along with three percentage columns and the number of hosts affected. The percentage columns show the percentages of the vulnerabilities that are exploitable, that were published more than 90 days ago, and that have had a patch available for more than 30 days. Ideally, all of these percentages should be 0%, because all exploitable vulnerabilities, old vulnerabilities, and vulnerabilities with patches available should have been mitigated already. If more details are desired (for example, what are the specific critical vulnerabilities that are exploitable?), click on the appropriate matrix cell to display more information. Some important vulnerability groupings are given, including default credential vulnerabilities, OS vulnerabilities, web technology (Java, Flash, PHP, etc.) vulnerabilities, web browser vulnerabilities, and office suite vulnerabilities. Most of these groupings are based on Common Platform Enumeration (CPE) strings. If desired, more vulnerability groupings can be added.
Vulnerability Summary - Exploitable Vulnerabilities: This matrix displays warning indicators for exploitable vulnerabilities actively and passively detected on the network, including vulnerabilities by OS, web vulnerabilities, application vulnerabilities, and vulnerabilities by keywords such as "Java" and "unsupported". Exploitable vulnerabilities that are externally accessible (i.e., accessible from hosts outside of the configured network address range) are very dangerous and must be remediated as soon as possible. Exploitable vulnerabilities that have been marked as accepted risks or recast to Informational within Security Center are also noted; these vulnerabilities should likely be re-evaluated. Clicking on a highlighted indicator will bring up the vulnerability analysis screen to display details for the vulnerabilities and allow further investigation. In the analysis screen, setting the tool to IP Summary will display the systems on which the vulnerabilities are present. Setting the tool to Vulnerability Details will display the full details for each vulnerability, including a description, the solution to fix the vulnerability, and in some cases, links to more information.