Microsoft’s July 2023 Patch Tuesday Addresses 130 CVEs (CVE-2023-36884)

Microsoft addresses 130 CVEs including five that were exploited in the wild as zero-day vulnerabilities and guidance on the malicious use of Microsoft signed drivers.
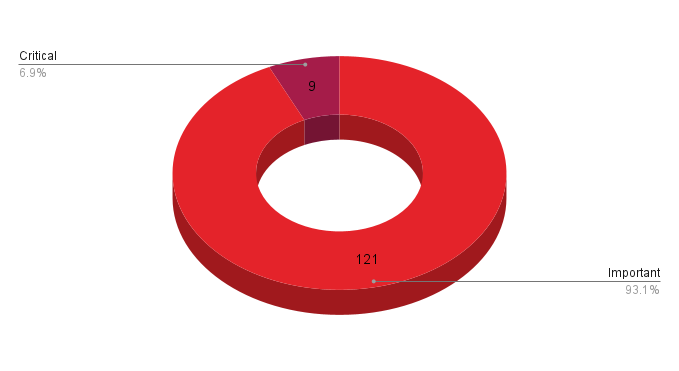
- 9Critical
- 121Important
- 0Moderate
- 0Low
Update July 17:The section for CVE-2023-36884 has been updated with guidance on using Tenable plugins to identify hosts which may be affected by this vulnerability.
Microsoft patched 130 CVEs in its July Patch Tuesday release, with nine rated as critical and 121 rated as important. Microsoft also issued an advisory with guidance on the malicious use of Microsoft signed drivers as well as an advisory regarding a security feature bypass in Trend Micro EFI modules.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- ASP.NET and.NET
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Media-Wiki Extensions
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Access
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Power Apps
- Microsoft Printer Drivers
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library
- NET and Visual Studio
- Paint 3D
- Role: DNS Server
- Windows Active Template Library
- Windows Admin Center
- Windows App Store
- Windows Authentication Methods
- Windows CDP User Components
- Windows Cluster Server
- Windows Cloud Files Mini Filter Driver
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Connected User Experiences and Telemetry
- Windows CryptoAPI
- Windows Cryptographic Services
- Windows CNG Key Isolation Service
- Windows Deployment Services
- Windows EFI Partition
- Windows Failover Cluster
- Windows Geolocation Service
- Windows HTTP.sys
- Windows Image Acquisition
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Layer-2 Bridge Network Driver
- Windows Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
- Windows Local Security Authority (LSA)
- Windows Message Queuing
- Windows MSHTML Platform
- Windows Netlogon
- Windows ODBC Driver
- Windows OLE
- Windows Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) SnapIn
- Windows Partition Management Driver
- Windows Peer Name Resolution Protocol
- Windows PGM
- Windows Power Apps
- Windows Print Spooler Components
- Windows Printer Drivers
- Windows Remote Desktop
- Windows Remote Procedure Call
- Windows Server Update Service
- Windows SmartScreen
- Windows SPNEGO Extended Negotiation
- Windows Transaction Manager
- Windows Update Orchestrator Service
- Windows VOLSNAP.SYS
- Windows Volume Shadow Copy
- Windows Win32K
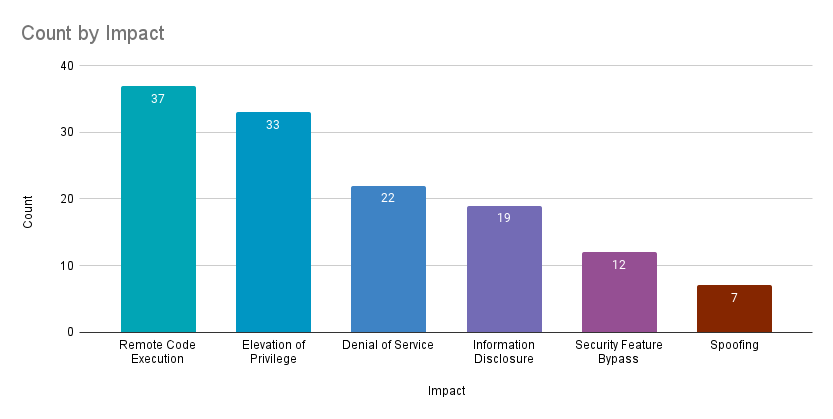
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 28.5% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 25.4%.
CVE-2023-36884 | Office and Windows HTML Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36884 is a RCE vulnerability in Microsoft Windows and Office that was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.3 and has been exploited in the wild as a zero-day. At the time this blog post was published and this advisory was made public, Microsoft had not released any patches for this vulnerability. However, Microsoft has provided mitigation guidance that can be used to avoid exploitation.
According to researchers at Microsoft, exploitation of CVE-2023-36884 has been attributed to a threat actor known as Storm-0978, also known as DEV-0978 and RomCom, a reference to the backdoor used by the group as part of its attacks. The threat actor is reportedly based out of Russia and is known for conducting ransomware attacks, including extortion-only campaigns, using a ransomware known as Underground. Additionally, the group also conducts intelligence gathering operations that rely on credential theft. Exploitation of CVE-2023-36884 began in June 2023. Targeted regions include Ukraine, North America and Europe while targeted industries include telecommunications and finance. For more information, please refer to Microsoft’s blog post.
Tenable has released Plugin ID 178275: Office and Windows HTML Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2023-36884) Mitigation which can be used to identify a Windows host that is potentially missing a mitigation for CVE-2023-36884. In order for the plugin to execute, users are required to enable the "Show potential false alarms" setting, also known as paranoid mode.
We recommend enabling only this specific plugin in a paranoid scan. Scan policies configured to have all plugins enabled will see an increase in the number of triggers, as it will include all paranoid plugins during the scan.
CVE-2023-35311 | Microsoft Outlook Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2023-35311 is a security feature bypass vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook. It was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.8 and was exploited in the wild as a zero-day. Exploitation of this flaw requires an attacker to convince a potential victim to click on a malicious URL. Successful exploitation would result in the bypassing of the Microsoft Outlook Security Notice prompt, a feature designed to protect users. Microsoft says that while its Outlook Preview pane feature is an attack vector, user interaction is still required.
CVE-2023-32046 | Windows MSHTML Platform Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-32046 is an EoP vulnerability in Microsoft’s MSHTML (Trident) engine that was exploited in the wild as a zero-day. It was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 7.8 and patches are available for all supported versions of Windows. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to create a specially crafted file and use social engineering techniques to convince their target to open the document. Microsoft’s advisory also includes a note suggesting that users who install Security Only updates should also install the Internet Explorer Cumulative update to fully address this vulnerability.
The discovery of CVE-2023-32046 follows CVE-2021-40444, another zero-day flaw in Microsoft’s MSHTML that was exploited in the wild and patched as part of Microsoft’s September 2021’s Patch Tuesday release. It was used by a variety of threat actors, from advanced persistent threat actors and ransomware groups. While CVE-2021-40444 didn’t make our top 5 list in the 2021 Threat Landscape Retrospective, the vulnerability was part of a group of noteworthy vulnerabilities that nearly made our list.
CVE-2023-36874 | Windows Error Reporting Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2023-36874 is an EoP vulnerability in the Microsoft Windows Error Reporting Service. It was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 7.8 and was exploited in the wild as a zero-day. To exploit this flaw, an attacker would need to have already gained local access to a target system and have certain basic user privileges. Successful exploitation would allow an attacker to obtain administrative privileges on the target system. Discovery of this flaw is credited to Vlad Stolyarov and Maddie Stone, researchers at Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG). At the time this blog post was published, no specific details about its exploitation were available.
CVE-2023-32049 | Windows SmartScreen Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2023-32049 is a security feature bypass vulnerability impacting Windows SmartScreen, an early warning system designed to protect against malicious websites used for phishing attacks or malware distribution. In order to exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to convince a user into opening a specially crafted URL. Exploitation would allow the attacker to bypass the “Open File” warning prompt and compromise the victim's machine. This vulnerability was exploited in the wild as a zero-day and was assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.8.
This vulnerability is similar to other mark of the web (MOTW) vulnerabilities patched by Microsoft in which malicious files could evade MOTW defenses. CVE-2022-44698 is a recent example of another zero-day vulnerability that was exploited in the wild and patched in the December 2022 Patch Tuesday release.
CVE-2023-29347 | Windows Admin Center Spoofing Vulnerability
CVE-2023-29347 is a spoofing vulnerability in Windows Admin Center (WAC) assigned a CVSSv3 score of 8.7 and a max severity rating of important. The vulnerability lies in the web server component of WAC, however malicious scripts would execute on a victims browser, so Microsoft’s CVSS scoring reflects this as a scope change. There are several ways a remote, authenticated attacker can exploit the vulnerability: through a malicious script imported into the WAC HTML form, through a.csv file imported to the user interface or through the WAC API. Successful exploitation allows the attacker to perform operations on the WAC server using the privileges of the victim.
CVE-2023-35365, CVE-2023-35366 and CVE-2023-35367 | Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2023-35365, CVE-2023-35366, CVE-2023-35367 are RCE vulnerabilities in the Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) of Windows operating systems, each of which were assigned a CVSSv3 score of 9.8. RRAS is a service in Windows that can be used as a VPN gateway or router. Exploitation requires an attacker to send crafted packets to an impacted server. RRAS is not installed or configured in Windows by default and those users who have not enabled the feature are not impacted by these vulnerabilities. Microsoft has given these vulnerabilities a rating of “Exploitation less likely” using the Microsoft Exploitability Index
CVE-2023-32057 | Microsoft Message Queuing Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
ADV230001 | Guidance on Microsoft Signed Drivers Being Used Maliciously
Microsoft released ADV230001 to provide guidance around the malicious use of Microsoft Signed Drivers. According to the advisory, some drivers which had been certified by Microsoft’s Windows Hardware Developer Program (MWHDP) were abused by malicious actors as part of post-compromise activity. In these instances, the malicious actors already gained administrative access to affected systems in order to use these malicious drivers. Microsoft investigated the issue and found that several developer program accounts were compromised and abused to submit malicious drivers to be signed with a Microsoft signature. Microsoft has since disabled these accounts from being able to submit any further drivers, released updates that untrust those malicious signed files as well as added blocking definitions to Microsoft Defender. We recommend reviewing the advisory and following the recommendations outlined by Microsoft.
Tenable Solutions
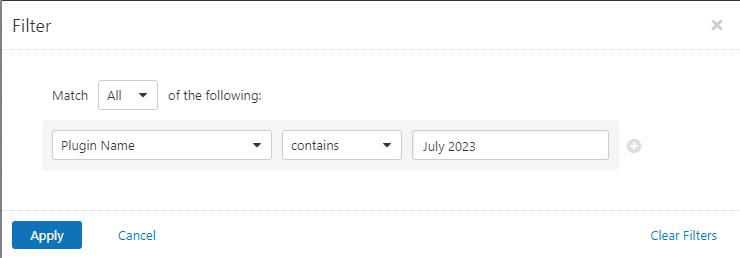
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced scan, in the plugins tab, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains July 2023.
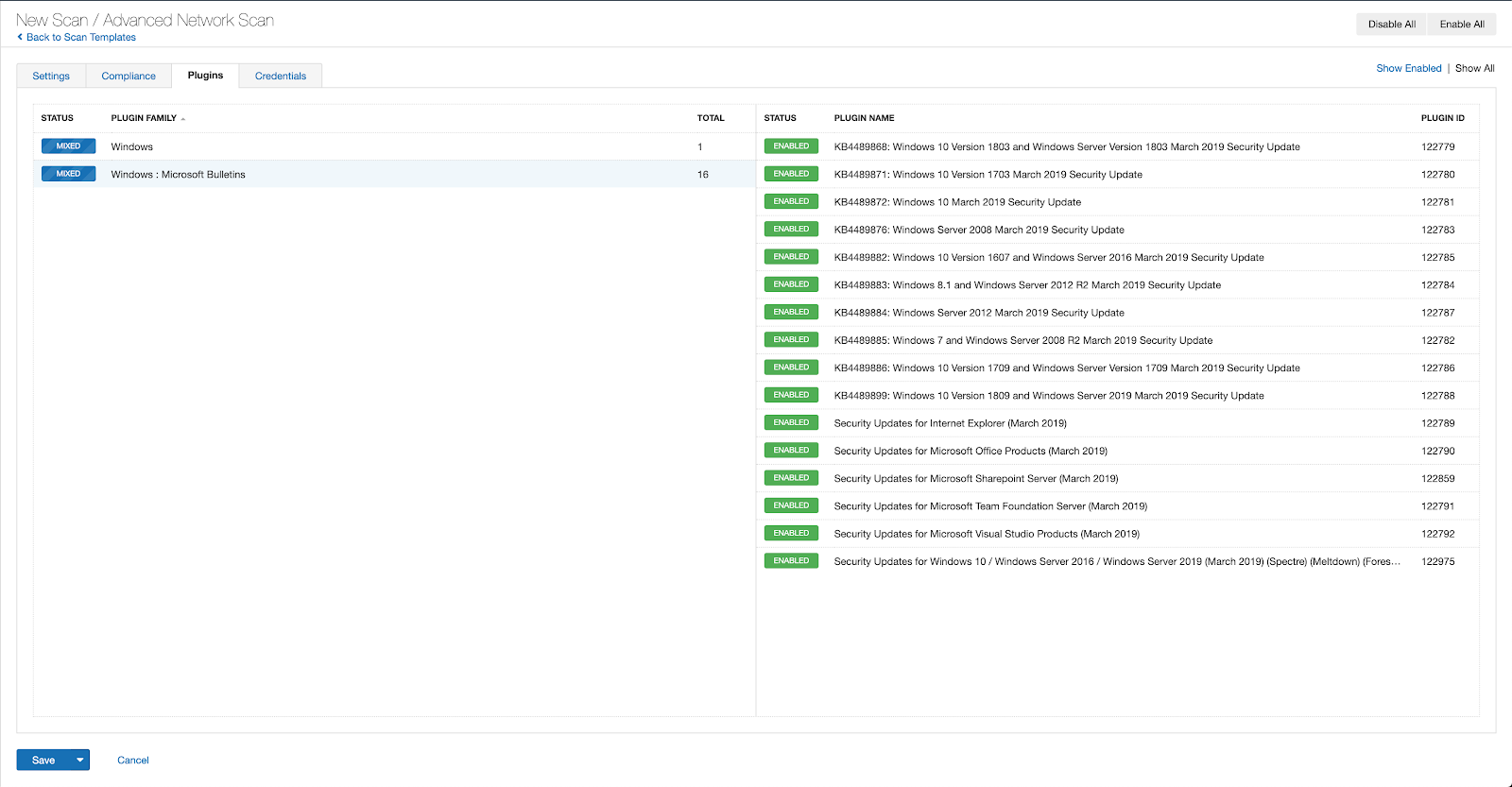
With that filter set, click the plugin families to the left and enable each plugin that appears on the right side. Note: If your families on the left say Enabled, then all the plugins in that family are set. Disable the whole family before selecting the individual plugins for this scan. Here’s an example from Tenable Vulnerability Management (formerly Tenable.io):
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s July 2023 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
Get more information
- Microsoft's July 2023 Security Updates
- Tenable plugins for Microsoft July 2023 Patch Tuesday Security Updates
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about https://www.tenable.com/products/tenable-one">Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.
Change Log
Update July 17:The section for CVE-2023-36884 has been updated with guidance on using Tenable plugins to identify hosts which may be affected by this vulnerability.
Update July 11: The section for CVE-2023-36884 has been updated to highlight the mitigation guidance provided by Microsoft as no patches were available at the time this blog post was published.
- Exposure Management
- Vulnerability Management


