CVE-2020-5776, CVE-2020-5777: Multiple Vulnerabilities in the MAGMI Magento Mass Import Plugin

Tenable Research discovers multiple vulnerabilities in the MAGMI Magento plugin that could lead to remote code execution on a vulnerable Magento site.
Background
On September 1, we published TRA-2020-51, a Tenable Research Advisory for two vulnerabilities in the Magento Mass Import (MAGMI) plugin. These vulnerabilities were discovered by Enguerran Gillier of the Tenable Web Application Security Team. MAGMI is a Magento database client written in PHP, which is used to perform raw bulk operations on the models of an online store. Our research into these vulnerabilities follows an FBI flash security alert that became public in May 2020 regarding in-the-wild exploitation of CVE-2017-7391, a cross-site scripting vulnerability in MAGMI that was used to target vulnerable Magento sites.
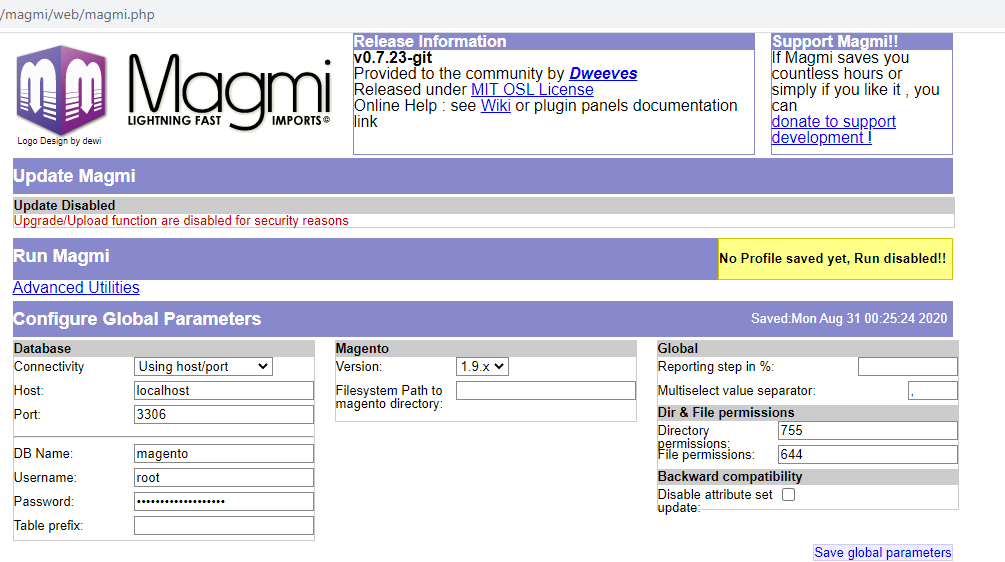
Analysis
CVE-2020-5776 is a cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability in MAGMI for Magento. This flaw exists because the GET and POST endpoints for MAGMI don’t implement CSRF protection, such as random CSRF tokens. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability to perform a CSRF attack by tricking a Magento Administrator into clicking on a link while they are authenticated to MAGMI. The attacker could hijack the administrator’s sessions, allowing them to execute arbitrary code on the server where MAGMI is hosted.
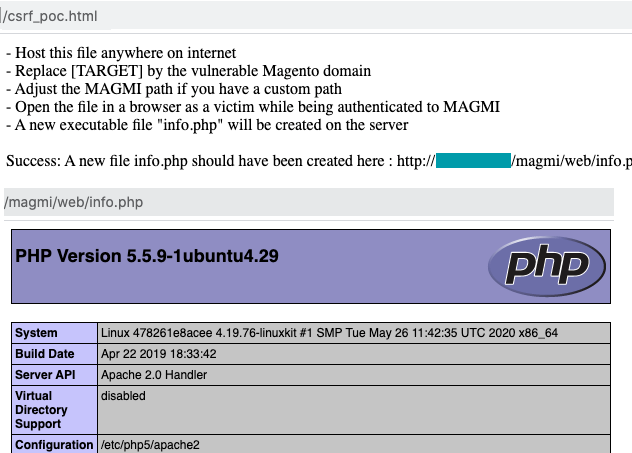
CVE-2020-5777 is an authentication bypass vulnerability in MAGMI for Magento version 0.7.23 and below due to the presence of a fallback mechanism using default credentials.
MAGMI uses HTTP Basic authentication and checks the username and password against the Magento database’s admin_user table. If the connection to the Magento database fails, MAGMI will accept default credentials, which are magmi:magmi. As a consequence, an attacker could force the database connection to fail due to a database denial of service (DB- DoS) attack, then authenticate to MAGMI using the default credentials.
The impact of this attack is remote code execution (RCE) on the server where MAGMI is hosted. During our testing, we successfully performed a Magento DB- DoS attack only when the following condition was true: the maximum number of concurrent MySQL connections was greater than the maximum number of concurrent Apache HTTP connections (or another HTTP or PHP server). By sending a large number of concurrent connection requests that exceed the MySQL connections limit, but not the maximum Apache HTTP connection limit, attackers could temporarily block access to the Magento database and simultaneously make an authenticated request to MAGMI using the default credentials.
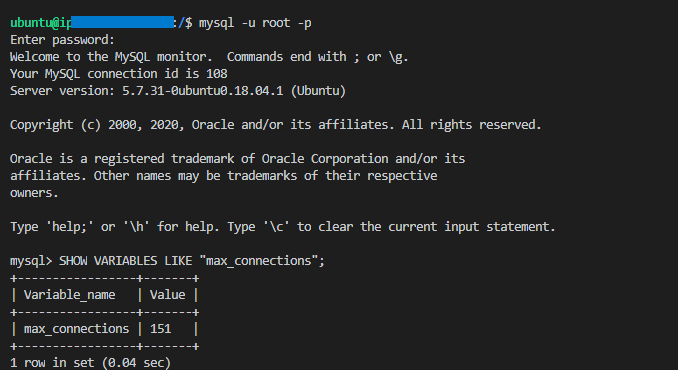
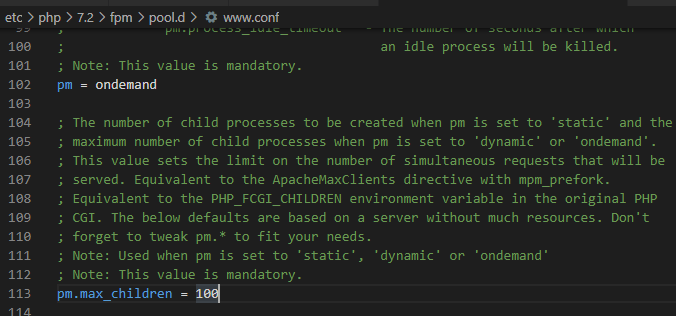
The MySQL connections limit can be found in a variable called “max_connections,” which is 151 by default. You can check this value by connecting to the MySQL instance and executing the following database query: SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "max_connections";
The Apache HTTP connections limit is located in a directive called “MaxRequestWorkers” (or MaxClients or pm.max_children) in the Apache Multi-Processing Module (MPM) configuration.
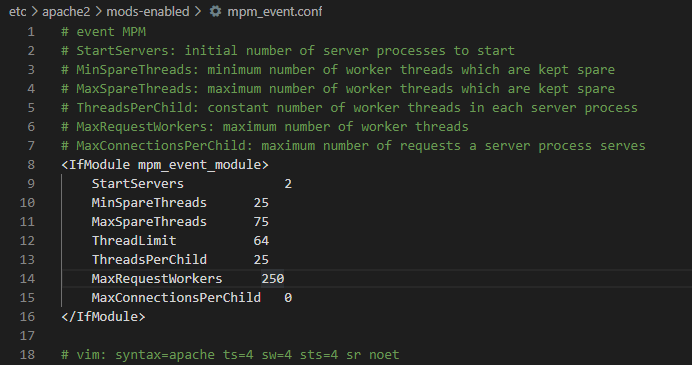
In our testing, we found that at least since Apache version 2.4.10, the default value is either 400 or 250. In prior versions of Apache, the default value was 150, which is smaller than the MySQL default max_connections. For more information about MaxRequestWorkers please check your Apache server documentation.
Proof of concept
A proof of concept (PoC) for these vulnerabilities can be found under the poc folder on Tenable’s GitHub page.
Vendor response
Tenable Research reached out to the developer of the MAGMI plugin on June 3. After follow-up communications on June 17 and July 6, we received acknowledgement on July 6 that the issues we identified were in the process of being fixed. We have since sent requests for updates and have not received any. However, the developers released a new version of the plugin on August 30 to address one of the two vulnerabilities (CVE-2020-5777). A summary of the disclosure process can be found in the Tenable Research Advisory, TRA-2020-51.
Solution
A patch has been published for CVE-2020-5777 in MAGMI version 0.7.24 on August 30. This patch should be applied as soon as possible. At the time this blog post was published, however, there was still no patch available for CVE-2020-5776. To reduce your risk in the meantime, we recommend disabling or uninstalling the plugin altogether until a patch is available, as well as refraining from active web browsing while authenticated to MAGMI.
It should also be noted that there is a fork of MAGMI for Magento 2 that is also vulnerable to these flaws. Because it is a fork of the original MAGMI plugin, users of the Magento 2 plugin should disable or uninstall the plugin until patches are available for the Magento 2 version.
Identifying affected systems
A list of Tenable plugins to identify these vulnerabilities will appear here as they’re released.
Get more information
- TRA-2020-51: Tenable Research Advisory for MAGMI Plugin Vulnerabilities
- FBI Flash Alert MU-000127-MW for MAGMI vulnerabilities (May 2020)
- ZDNet Article about FBI Flash Alert (May 2020)
Join Tenable's Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.
- Vulnerability Management

